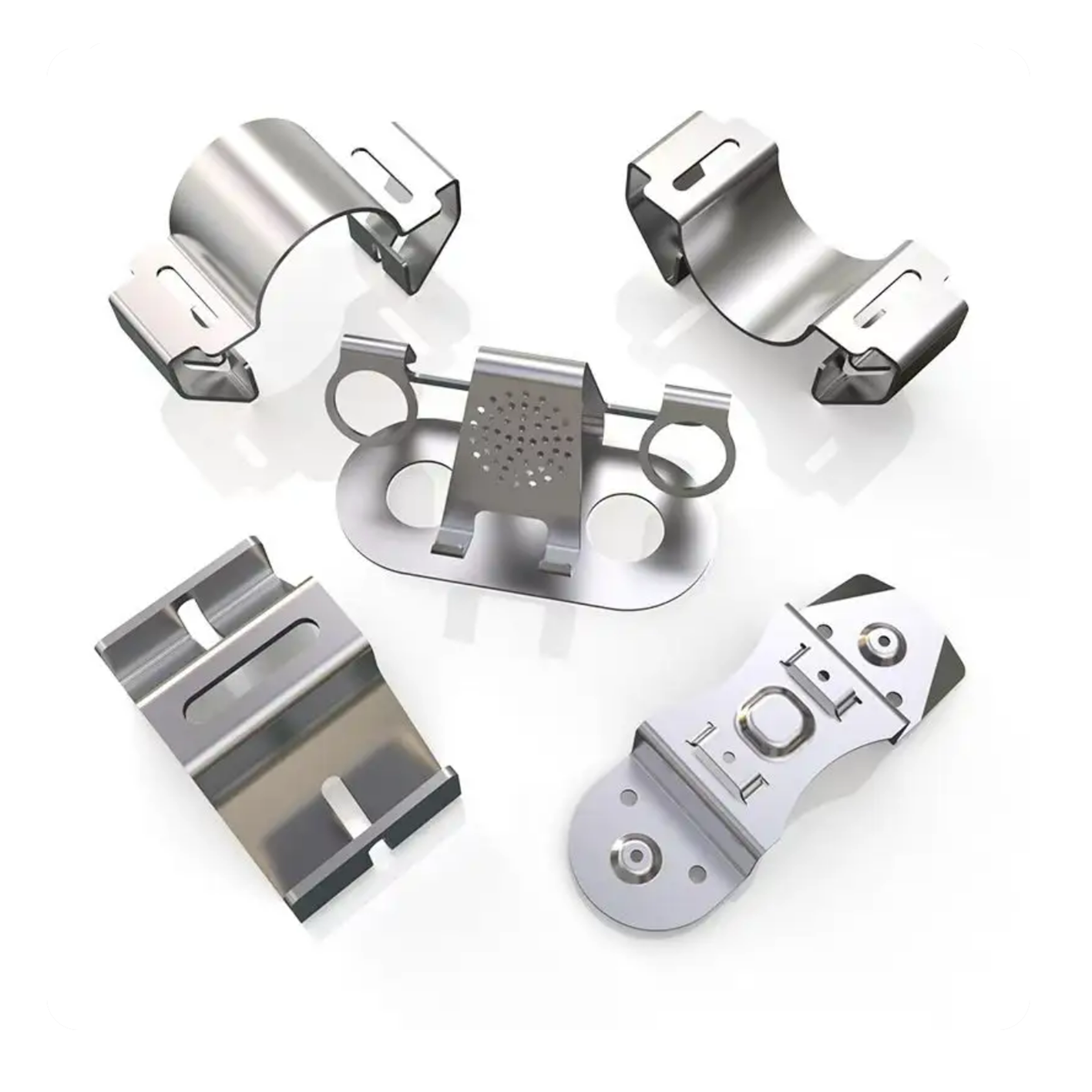
Custom metal laser cutting bending Carbon steel sheet metal fabrication parts
Description
| Product Type | customized product | |||||||||||
| One-Stop Service | Mold development and design-submit samples-batch production-inspection-surface treatment-packaging-delivery. | |||||||||||
| Process | stamping,bending,deep drawing,sheet metal fabrication,welding,laser cutting etc. | |||||||||||
| Materials | carbon steel,stainless steel,aluminum,copper,galvanized steel etc. | |||||||||||
| Dimensions | according to customer's drawings or samples. | |||||||||||
| Finish | Spray painting, electroplating, hot-dip galvanizing, powder coating, electrophoresis, anodizing, blackening, etc. | |||||||||||
| Application Area | Auto parts, agricultural machinery parts, engineering machinery parts, construction engineering parts, garden accessories, environmentally friendly machinery parts, ship parts, aviation parts, pipe fittings, hardware tool parts, toy parts, electronic parts, etc. | |||||||||||
Stamping basics
Stamping (also called pressing) involves placing flat metal in coil or blank form into a stamping machine. In a press, tool and die surfaces shape metal into the desired shape. Punching, blanking, bending, stamping, embossing and flanging are all stamping techniques used to shape metal.
Before the material can be formed, stamping professionals must design the mold through CAD/CAM engineering. These designs must be as precise as possible to ensure proper clearance for each punch and bend for optimal part quality. A single tool 3D model can contain hundreds of parts, so the design process is often quite complex and time-consuming.
Once a tool's design is determined, manufacturers can use a variety of machining, grinding, wire-cutting, and other manufacturing services to complete its production.
Quality management




Vickers hardness instrument.
Profile measuring instrument.
Spectrograph instrument.
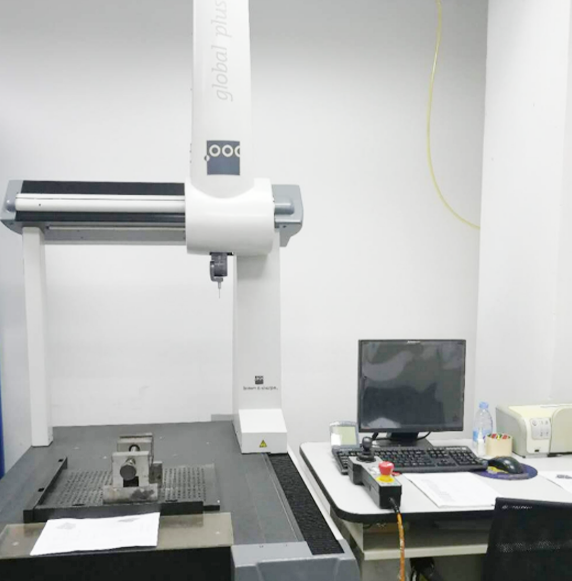
Three coordinate instrument.
Shipment Picture




Production Process



01. Mold design
02. Mould Processing
03. Wire cutting processing
04. Mold heat treatment




05. Mold assembly
06. Mold debugging
07. Deburring
08. electroplating


09. Product Testing
10. Package
Types of stamping
We offer single and multistage, progressive die, deep draw, fourslide, and other stamping methods to ensure the most effective method for manufacturing your products. Xinzhe’s experts can match your project with the appropriate stamping by reviewing your uploaded 3D model and technical drawings.
- Progressive Die Stamping uses multiple dies and steps to create deeper parts than would typically be achievable through single dies. It also enables multiple geometries per part as they go through various dies. This technique is best suited to high volume and large parts such as those in the automotive industry. Transfer die stamping is a similar process, except progressive die stamping involves a workpiece attached to a metal strip pulled through the entire process. Transfer die stamping removes the workpiece and moves it along a conveyor.
- Deep Draw Stamping creates stampings with deep cavities, like enclosed rectangles. This process creates rigid pieces since the extreme deformation of the metal compresses its structure into a more crystalline form. Standard draw stamping, which involves shallower dies used to shape the metal, is also commonly utilized.
- Fourslide Stamping shapes parts from four axes instead of from one direction. This method is used to manufacture small intricate parts including electronics components such as phone battery connectors. Offering more design flexibility, lower production costs, and faster manufacturing times, fourslide stamping is popular in aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics industries.
- Hydroforming is an evolution of stamping. Sheets are placed on a die with a bottom shape, while the upper shape is a bladder of oil that fills to high pressure, pressing the metal into the shape of the lower die. Multiple parts can be hydroformed simultaneously. Hydroforming is a quick and accurate technique, though it requires a trim die to cut the parts out of the sheet afterward.
- Blanking cuts pieces out from the sheet as an initial step before forming. Fineblanking, a variation of blanking, makes precise cuts with smooth edges and a flat surface.
- Coining is another type of blanking that creates small round workpieces. Since it involves significant force to form a small piece, it hardens the metal and removes burrs and rough edges.
- Punching is the opposite of blanking; it involves removing material from the workpiece instead of removing material to create a workpiece.
- Embossing creates a three-dimensional design in the metal, either raised above the surface or through a series of depressions.
- Bending happens on a single axis and is often used to create profiles in U, V, or L shapes. This technique is accomplished by clamping one side and bending the other over a die or pressing the metal into or against a die. Flanging is bending for tabs or parts of a workpiece instead of the whole part.
Tight tolerances
Whether you are in the aerospace, automotive, telecommunications or electronics industry, our precision metal stamping services can deliver the part shapes you require. Our suppliers work hard to meet your tolerance requirements by iterating tool and mold designs to fine-tune output to meet your needs. However, the tighter the tolerances, the more difficult and costly it is. Precision metal stampings with tight tolerances can be brackets, clips, inserts, connectors, accessories and other parts in consumer appliances, power grids, aircraft and automobiles. They are also used to make implants, surgical instruments, temperature probes and other medical device parts such as housings and pump components.
Regular checks after each successive run to ensure the output is still within specification is typical for all stampings. Quality and consistency are part of a comprehensive production maintenance program that monitors stamping tool wear. Measurements using inspection jigs are standard measurements on long-running stamping lines.







